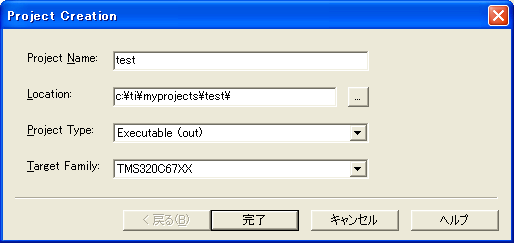
| back | �T�[�o�I�� (��{[ 1 , 2 , IP ], �~���[[ 1 , 2 , IP ] |
DSP ���S�҂̂��߂̓���̃y�[�W |


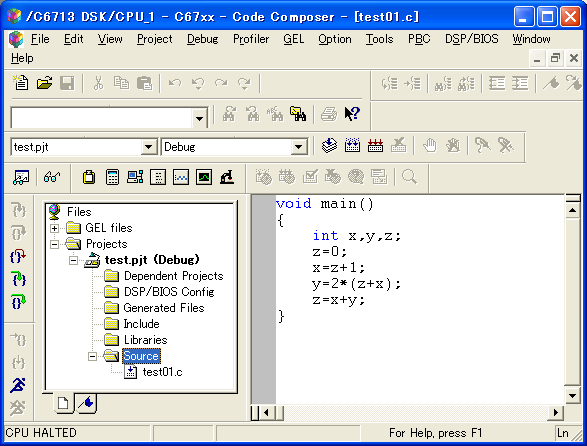
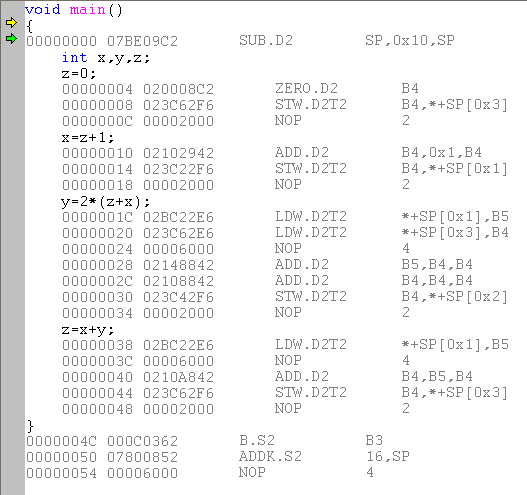
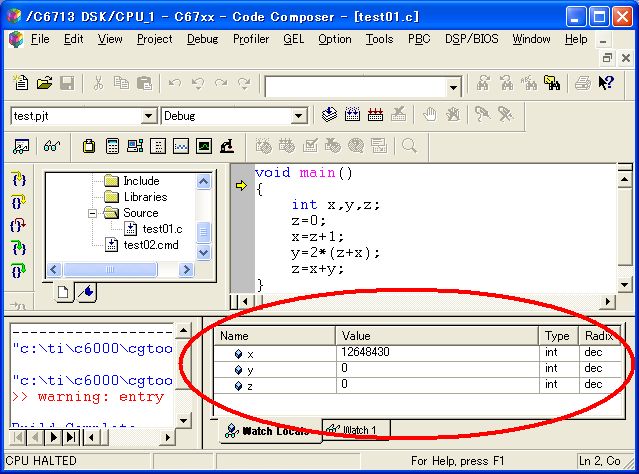
void main()
{
int x,y,z;
z=0;
x=z+1;
y=2*(z+x);
z=x+y;
}
MEMORY
{
RAM: origin = 0x0, length = 0x10000
}
#define BSize 96
void main()
{
float s1buff[BSize];
float c1buff[BSize];
float s2buff[BSize];
float c2buff[BSize];
float yybuff[BSize];
int i;
float a,b;
float c,d;
a=0.99786;
b=0.06540;
c=0.94693;
d=0.32144;
s1buff[0]=0.0;
c1buff[0]=1.0;
s2buff[0]=0.0;
c2buff[0]=1.0;
yybuff[0]=s1buff[0]*s2buff[0];
for (i=1; i<BSize; i++) {
s1buff[i]=a*s1buff[i-1]+b*c1buff[i-1];
c1buff[i]=a*c1buff[i-1]-b*s1buff[i-1];
s2buff[i]=c*s2buff[i-1]+d*c2buff[i-1];
c2buff[i]=c*c2buff[i-1]-d*s2buff[i-1];
yybuff[i]=s1buff[i]*s2buff[i];
}
}
MEMORY
{
RAM: origin = 0x0, length = 0x10000
}
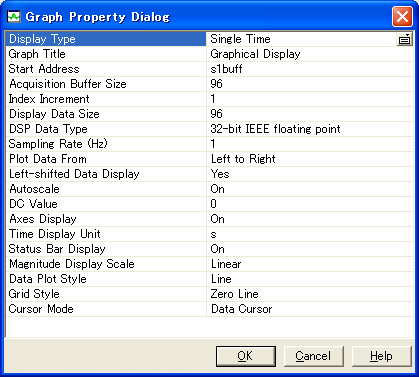
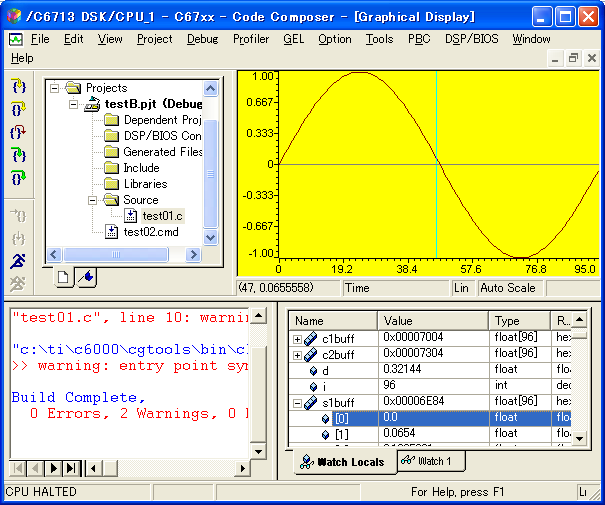
| 1 �s�� | Display Type | �O���t�̌^���w�肵�܂��B ����ȊO�ɁCFFT �Ȃǂ��I�ׂ܂� |
| 2 �s�� | Start Address | �����̕�����́C �O���t�̃^�C�g���Ƃ��Ďg���܂� |
| 3 �s�� | Start Address | �z���w�肵�܂� |
| 4 �s�� | Acquisition ... | �ǂݍ��ރf�[�^�̐� |
| 6 �s�� | Display Data Size | �\������f�[�^�̐� |
| 7 �s�� | DSP Data Type | ����� C ����̗��ł� float �^�̔z��Ȃ̂� 32-bit IEEE floating point ���w�肵�܂����B �ʂ̌^�̔z���������Ȃ�C �����őΉ�����^���w�肵�܂� |
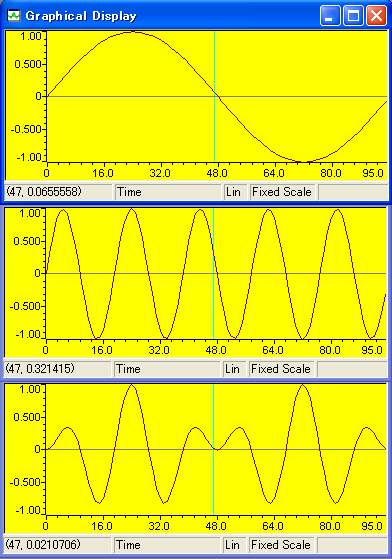
| 3 �s�� | Start Address | s2buff |
| 3 �s�� | Start Address | ybuff |
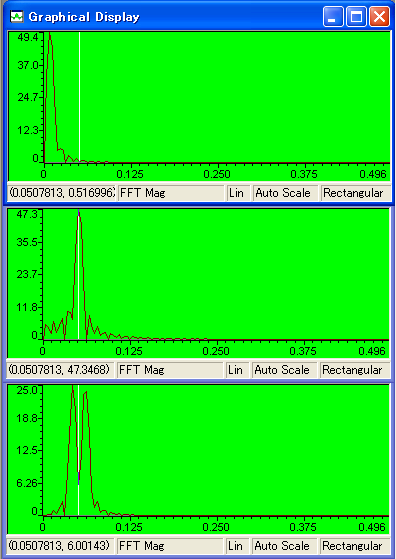
| 1 �s�� | Display Type | FFT Magnitude |
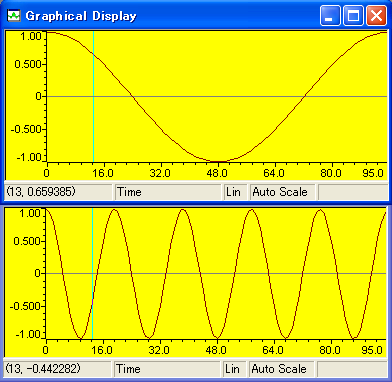
#include <math.h>
#define BSize 96
void main()
{
float s1buff[BSize];
float s2buff[BSize];
float yybuff[BSize];
int i;
float rad;
rad=0;
for (i=0; i<BSize; i++) {
s1buff[i]=sin(rad);
s2buff[i]=sin(5.*rad);
yybuff[i]=s1buff[i]*s2buff[i];
rad+=2.*3.14159/96.;
}
}
MEMORY
{
RAM: origin = 0x0, length = 0x10000
}
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf("Hello World ! \n");
}
MEMORY
{
RAM: origin = 0x0, length = 0x10000
}